Next: Interfaces. Up: Graphical user interfaces. Previous: None.
Textbook: Section 12.2
Many common programs involve graphical user interfaces. We're going to look at Java's libraries for building GUIs, called Swing. (There's an older library Java used for this, called AWT. This is what the textbook covers. We're going to look at Swing in this class, though.)
The first class we'll look at is the JFrame, which represents a window. Consider the following simple program.
import java.awt.*; // we'll include these three import lines in
import java.awt.event.*; // all our programs using Swing.
import javax.swing.*;
public class EmptyWindow extends JFrame {
public EmptyWindow() {
pack();
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
EmptyWindow window = new EmptyWindow();
window.show();
}
}
A JFrame has just a few methods worth talking about for now.
A Container is an object used for holding components. (Examples of components include buttons and text fields.) For the moment, we're just going to pay attention to one of its methods.
| BorderLayout.NORTH | BorderLayout.EAST |
| BorderLayout.SOUTH | BorderLayout.WEST |
| BorderLayout.CENTER | |
Finally, there are the components. The first one of these we'll see is the JButton, which represents a button on the screen. For the moment, we'll just worry about the constructor method.
Another type of component is the text field, where the user can type something. The JTextField class is
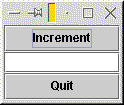
Here's a program that creates a window containing two buttons and a text field. We're going to work on making the buttons do something soon. For the moment, all the program does is display the components.
import java.awt.*;
import java.awt.event.*;
import javax.swing.*;
public class ButtonExample extends JFrame {
JButton incr_button;
JButton quit_button;
JTextField number_field;
public ButtonExample() {
incr_button = new JButton("Increment");
quit_button = new JButton("Quit");
number_field = new JTextField();
Container contents = getContentPane();
contents.add(incr_button, BorderLayout.NORTH);
contents.add(number_field, BorderLayout.CENTER);
contents.add(quit_button, BorderLayout.SOUTH);
pack();
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
(new ButtonExample()).show();
}
}

Next: Interfaces. Up: Graphical user interfaces. Previous: None.