Test 2 Review B: Questions
Convert the following Haskell expression using do notation
to the equivalent non-do form using the Monad operator >>=.
do args <- getArgs
fstr <- readFile (head args)
putStrLn (show (length fstr))
Convert the following Haskell expression using do notation
to the equivalent non-do form using the Monad operator >>=.
do a <- getLine
b <- getLine
putStrLn b
putStrLn a
main with type IO () which reads two
lines from the user and then displays them back in opposite order (the
second line, then the first line).
Write a function readLines of type IO [String]
that reads lines typed by the user until the user types
“.” and then returns a list of the lines typed
wrapped in an IO, not including the “.” line.
You will use the getLine function (of type
IO String) to read a single line.
Define a Haskell function skipToLine whose type
signature is as below.
skipToLine :: Int -> IO StringGiven a positive integer, skipToLine should read that many
lines from the user using the getLine function of type
IO String, and its result should be the IO String packaged
in the final call to getLine.
Complete the following class definition by writing the
>>= function for the Maybe type.
data Maybe a = Just a | Nothing
instance Monad (Maybe a) where
return x = Just x
For this type, the expression x >>= f should
yield Just (f data) if x is Just data,
and it should yield Nothing if x is Nothing.
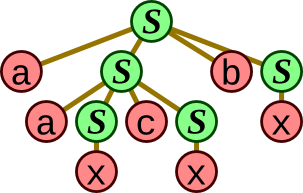
Based on the BNF grammar below, draw a syntax tree for the sentence a a x b x b x.
S → a S b S | x
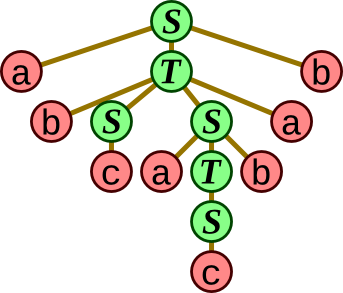
Based on the BNF grammar below, draw a syntax tree for the sentence a b c a c b a b.
S → a T b | c T → b S S a | S
Using BNF syntax, write a context-free grammar for the language of zero or more a's listed separated by commas, but without beginning or ending in a comma. The four shortest strings in the language are the empty string, “a”, “a,a”, “a,a,a”.
Test 2 Review B: Solutions
getArgs >>= (\args -> readFile (head args)
>>= \fstr -> putStrLn (show (length fstr)))
getLine >>= (\a -> getLine >>= (\b putStrLn second >> putStrLn a))
main = do first <- getLine
second <- getLine
putStrLn second
putStrLn first
readLines = do line <- getLine
if line == "."
then return []
else do rest <- readLines
return line : rest
skipToLine 1 = getLine
skipToLine n = do dummy <- getLine
skipToLine (n - 1)
Or:
skipToLine n = mapM getLine [1..(n - 1)] >> getLine
Nothing >>= f = Nothing
(Just x) >>= f = Just (f x)
S → | L L → a , L | a

